Building a new home is an exciting venture, but amidst the thrill of selecting floor plans and choosing paint colors, one crucial aspect often gets overlooked – insulation. Proper insulation is the key to creating a comfortable, energy-efficient living space. It not only regulates indoor temperatures but also plays a significant role in reducing energy bills and minimizing environmental impact.
In this step-by-step guide, we’ll walk you through the process of choosing the right insulation for your new home, ensuring that you make informed decisions that align with your specific needs and budget.

Step 1: Understand Your Home Climate
The first step in choosing the right insulation for your new home is to understand the climate of the region where you’ll be building. Different climates require different insulation solutions. For instance, homes in colder climates may need insulation that provides better thermal resistance, while homes in warmer climates may prioritize materials that offer effective heat reflection and ventilation.
If you’re unsure about your region’s climate, consult the U.S. Department of Energy’s climate zone map or a similar resource specific to your country. This information will guide you in selecting insulation materials with the appropriate R-value (a measure of thermal resistance) for your location.
Step 2: Know Your Insulation Options
Insulation comes in various forms, each with its unique properties and applications. Familiarize yourself with the most common types of insulation:
- Fiberglass Insulation: Composed of tiny glass fibers, fiberglass insulation is a popular and cost-effective choice. It comes in rolls or batts and is suitable for walls, floors, and attics.
- Cellulose Insulation: Made from recycled paper or plant fibers, cellulose insulation is an eco-friendly option. It can be blown or sprayed into walls and attics.
- Foam Board Insulation: This type of insulation is rigid and comes in panels. It’s commonly used in walls, roofs, and foundations.
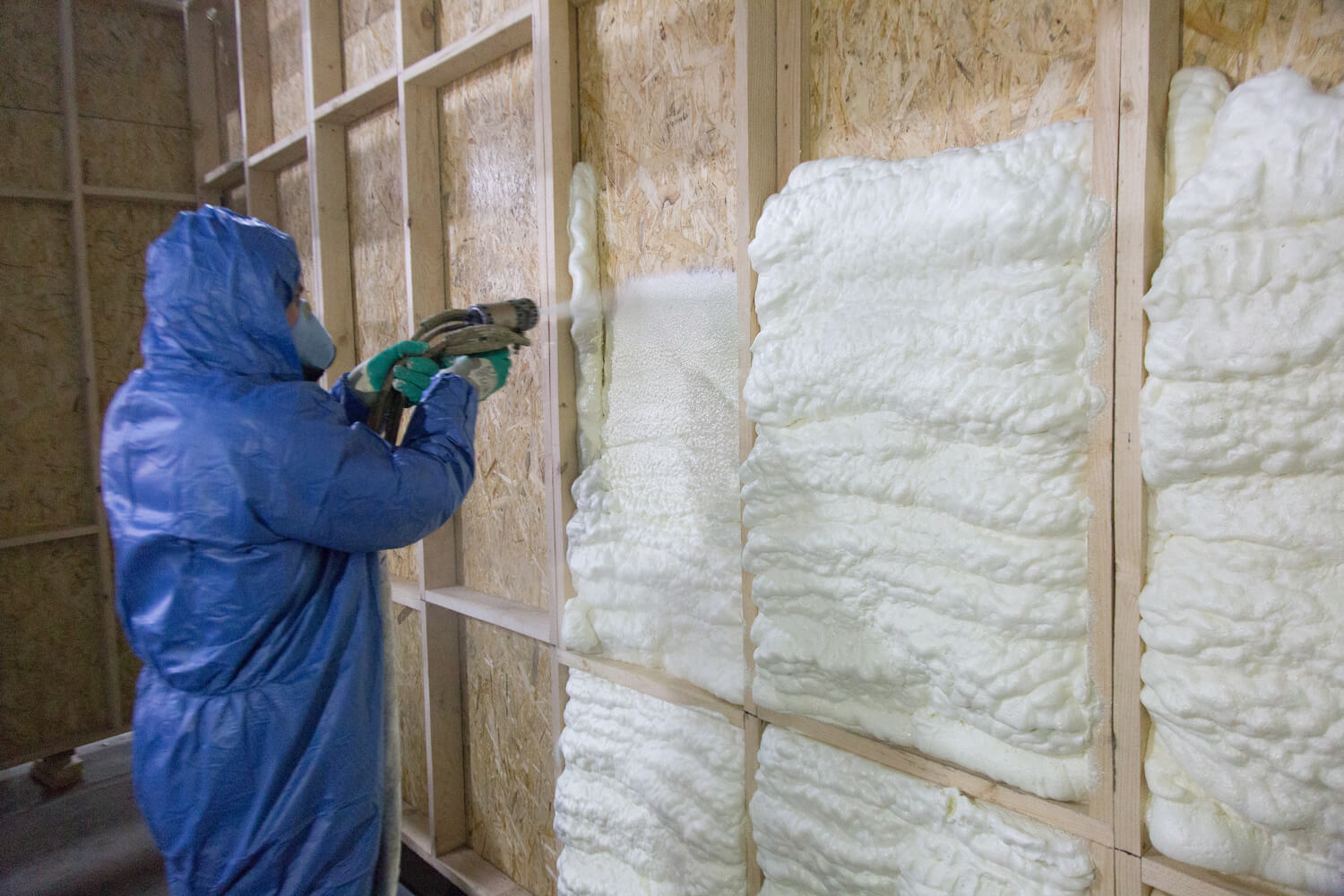
- Spray Foam Insulation: Applied as a liquid that expands into a foam, this insulation is ideal for filling gaps and hard-to-reach spaces.
- Mineral Wool Insulation: Made from molten glass or stone, mineral wool is fire-resistant and offers excellent thermal and sound insulation.
Each type of insulation has its pros and cons, so consider factors like cost, installation ease, and performance when making your decision.
Step 3: Set Your Home Budget
Insulation costs can vary significantly, so it’s essential to establish a budget early in the planning process. While certain types of insulation may have higher upfront costs, they can provide long-term savings through energy efficiency. Consider the long-term return on investment (ROI) when deciding on your budget. Additionally, factor in the cost of professional installation if you’re not planning to install the insulation yourself.
Step 4: Assess Building Codes and Insulation Regulations
Before finalizing your insulation choices, research and understand the building codes and regulations in your area. Building codes often dictate minimum R-values for different parts of a home, and compliance is crucial to obtaining necessary permits. Failure to meet these standards may result in increased energy bills, discomfort, and potential legal issues down the line.
Step 5: Consider New Home Environmental Impact
In an era where environmental consciousness is paramount, considering the ecological impact of your insulation choice is crucial. Some insulation materials, such as fiberglass and cellulose, contain recycled content, making them more sustainable choices. Others, like spray foam, may have a higher environmental cost in terms of production and disposal.
Explore insulation options with lower embodied energy and environmental impact. Additionally, investigate local recycling options for insulation materials to reduce waste during and after construction.
Step 6: Evaluate Home Insulation Performance
Different insulation materials have varying levels of thermal resistance, sound absorption, and fire resistance. Evaluate each material’s performance characteristics to ensure they align with your specific needs and priorities. Pay attention to factors such as:
- R-Value: The higher the R-value, the better the insulation’s thermal resistance. Ensure that the selected R-values meet or exceed the recommended levels for your climate.
- Sound Insulation: If you live in a noisy area or want to create a quieter home environment, consider insulation materials with excellent sound absorption properties.
- Fire Resistance: Some insulation materials, like mineral wool, are naturally fire-resistant, providing an added layer of safety to your home.
- Moisture Resistance: In areas prone to high humidity or moisture, opt for insulation materials that resist mold and mildew growth.
Step 7: Plan for Home Installation
Consider whether you’ll be installing the insulation yourself or hiring a professional. While some insulation materials, like fiberglass batts, are relatively DIY-friendly, others, such as spray foam, may require specialized equipment and expertise.
Professional installation ensures proper placement and sealing, minimizing the risk of gaps or inadequate coverage. Obtain quotes from reputable insulation contractors and factor these costs into your overall budget.
Step 8: Prioritize Home Air Sealing
Effective insulation goes hand in hand with proper air sealing. Identify and seal air leaks before installing insulation to maximize energy efficiency. Common areas for air leaks include windows, doors, electrical outlets, and gaps in the building envelope. A well-insulated and tightly sealed home not only conserves energy but also enhances indoor comfort.
Step 9: Optimize for Home Energy Efficiency
Choose insulation materials and techniques that contribute to the overall energy efficiency of your home. Consider features such as reflective barriers, which deflect radiant heat, and thermal bridging solutions to prevent heat loss through structural elements. A comprehensive energy-efficient approach will result in a home that is comfortable year-round while minimizing energy consumption.
Step 10: Plan for Future Maintenance
Finally, consider the long-term maintenance requirements of your chosen insulation materials. While many insulation types require minimal upkeep, others may need attention over time. Factor in considerations such as durability, susceptibility to pests, and the potential need for replacement or upgrades in the future.
Additional Considerations
Ventilation and Indoor Air Quality
While insulating your home is essential for temperature control, it’s equally crucial to maintain good indoor air quality. Proper ventilation is key to achieving this balance. Invest in a ventilation system that ensures a steady exchange of indoor and outdoor air. This not only helps regulate humidity levels but also prevents the buildup of pollutants within your home. Some insulation materials, like spray foam, can act as effective air barriers, contributing to improved indoor air quality by minimizing the infiltration of outdoor pollutants.
Government Incentives and Rebates
Explore government incentives and rebates that may be available for energy-efficient home improvements. Many regions offer financial incentives to encourage homeowners to choose insulation materials and techniques that reduce energy consumption. These incentives can offset the initial costs of high-performance insulation and contribute to long-term savings. Check with local authorities or energy efficiency programs to see if you qualify for any such programs.
Energy-Efficient Home Windows and Doors
While insulation plays a significant role in regulating indoor temperatures, don’t overlook the impact of energy-efficient windows and doors. Properly sealed windows and doors, paired with high-quality insulation, create a comprehensive thermal envelope for your home. Consider double-pane or triple-pane windows with low-emissivity coatings to minimize heat transfer. Additionally, ensure that doors are properly weather-stripped to prevent drafts.
Future Expansion and Home Renovation
Anticipate potential future changes to your home, such as additions or renovations, when planning your insulation strategy. Consider how these changes might affect the overall insulation system. Flexible insulation solutions, such as spray foam or loose-fill insulation, can adapt to structural modifications more easily than rigid insulation materials. Planning for future expansion ensures that your home remains energy-efficient and comfortable even as your needs evolve.
Seek Professional Guidance
If you find the process overwhelming or if you’re unsure about specific aspects of insulation, don’t hesitate to seek professional guidance. Engage with an energy consultant or a certified insulation contractor who can assess your home’s unique characteristics and recommend the most suitable insulation solutions. Their expertise can help you navigate complex decisions, ensuring that your insulation choices align with industry best practices and local building codes.
Conclusion
In the pursuit of an energy-efficient and comfortable home, insulation is a cornerstone. By expanding your considerations to include ventilation, incentives, windows, doors, and plans, you create a holistic approach to home insulation. Each decision contributes to the overall performance of your home, impacting not only your immediate comfort but also your long-term energy costs and environmental impact.
Remember, the right insulation is an investment in your home’s future. It’s a decision that not only pays off in terms of reduced energy bills but also contributes to a more sustainable and resilient living space. Take the time to explore your options, consider all relevant factors, and seek professional advice when needed. With a well-thought-out insulation strategy, you’re not just building a house; you’re creating a home that stands the test of time.